
In the ever-evolving arena of influencer marketing, staying ahead of the curve is crucial. Influencer Marketing Hub’s “Influencer Marketing Benchmark Report 2024“ outlines the current state of the industry and reveals the strategies savvy brands are using to navigate this dynamic landscape.
Part 1 of NAB Amplify’s two-part look at the data explored the key drivers fueling the industry’s remarkable growth, including how brands measure ROI and the dominance of platforms like Instagram and TikTok.
READ MORE: Recognizing ROI in Influencer Marketing: Growth, Trends and Challenges (NAB Amplify)
Here in Part 2 we delve into the emerging trends and technologies that will shape the influencer marketing landscape in the years to come, including artificial intelligence, virtual influencers, and the critical role of micro and nano-influencers.
AI and ML Enter the Chat
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing how brands identify, engage with, and analyze influencer partnerships, driving greater precision and efficiency in campaigns.
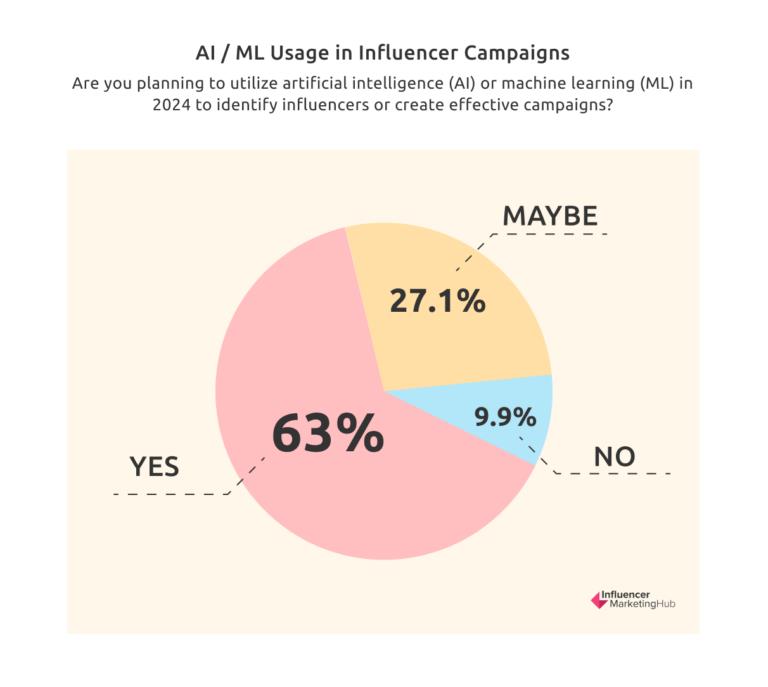
Influencer Marketing Hub reports that more than 60% of brands are planning on integrating AI into their strategies, with the technology primarily used for identifying the most effective influencers through advanced social media data analytics. This enables brands to target their campaigns more precisely and maximize their ROI. Additionally, AI is enhancing content distribution and helping to identify and mitigate fraudulent activities, ensuring more authentic and impactful influencer partnerships.
A robust 63% of survey respondents say they plan to use AI in executing their influencer campaigns, alongside 27.1% who think they might. Only 9.9% gave an unequivocal no to the question. What’s more, more than half of respondents who do plan to implement AI will use it to help identify influencers for brand partnerships.
“Clearly, Al and ML have hit the mainstream,” the reports notes. “Brands involved in influencer marketing can use Al in most phases of the process, from assisting influencer discovery to creating reports at the end of campaigns,” However, the authors add, “we were surprised by how little change there has been in Al usage this year by the marketers who participated in our study, compared to results over the last few reports.”
Despite this slowdown, the integration of AI and data analytics is a major trend, enhancing the precision and effectiveness of influencer marketing strategies by providing deeper insights into audience behavior, preferences and engagement patterns. A plethora of AI and ML tools — available via third-party platforms — are being employed to predict campaign outcomes more accurately and measure ROI with greater clarity.
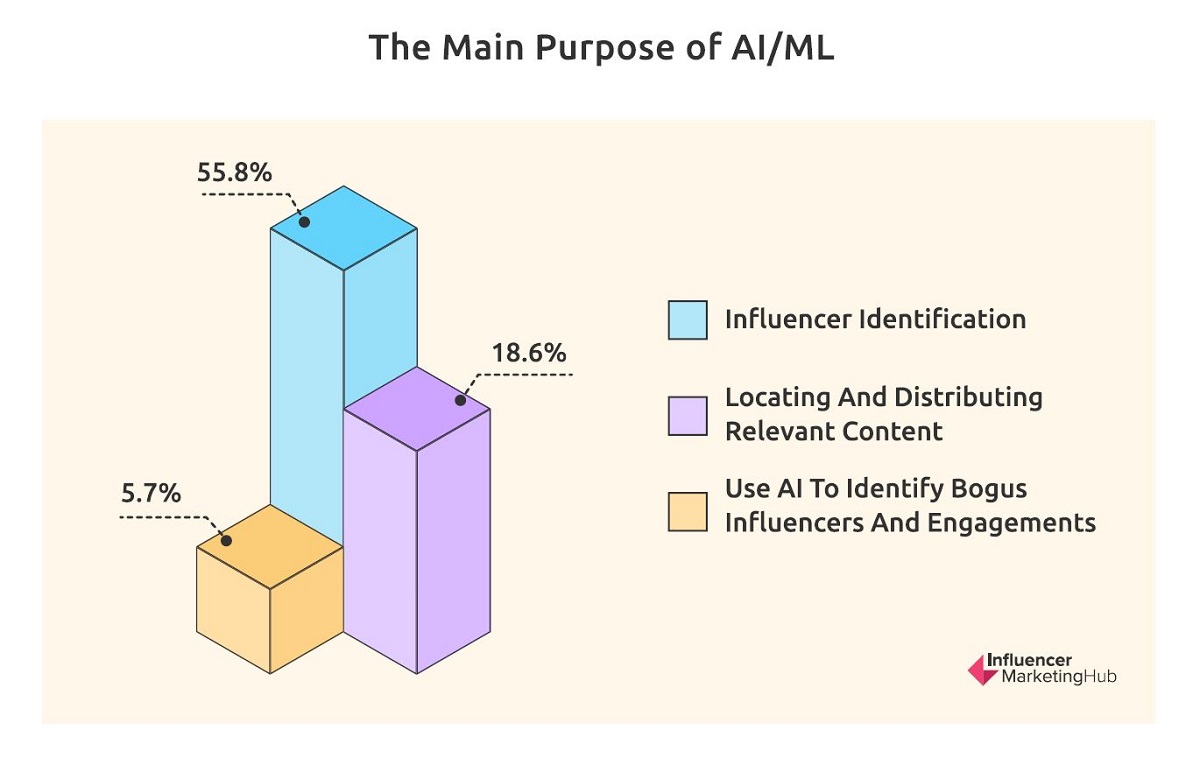
The primary use case for brands is discovery, with 55.8% of marketers using social media data analytics to identify the most effective influencers for a particular brand or campaign. Although somewhat less common, as the report notes, the second-most popular intended use of Al in influencer marketing is locating and distributing relevant content (18.6%), up from last year’s 13.3%.
However, only 5.7% of respondents intend to use Al to identify deceptive influencers and engagement, nearly the same percentage as last year’s results. “It will be interesting to see if this figure rises over time, as more people discover what Al can achieve.”
Automation remains a contentious issue in influencer marketing, the report finds. “Some people believe you can automate virtually everything from influencer selection to influencer payment. Others value the personal touch and think influencer marketing is a hands-on process.”
2024 saw a small decrease in the number of respondents who believe that automation plays a vital role in influencer marketing (73.4%, down from 77% in 2023). “Most businesses using influencer marketing are happy to use tools and platforms (or work with agencies that do so) nowadays. Initial suspicions about AI and automation have dramatically lessened over the last few years. This small reduction may be antipathy towards the widespread use of AI nowadays,” the report suggests.
Virtual Influencers on the Rise
One of the most intriguing emerging trends is the rise of virtual influencers. According to Influencer Marketing Hub, 25% of brands are now exploring campaigns involving virtual influencers and more than 60% of marketers have used virtual influencers in the past.
Lu from Brazilian retail giant Magalu is perhaps the most famous example, with 31 million followers at her peak. Advertising agency Ogilvy created Lu as a virtual assistant in 2003 and then built her up as the face of the brand, creating social media accounts for her. Over time she became a powerful influencer, evolving into a cultural celebrity, trendsetter, fashion icon and social media diva, working with brands like Adidas, Samsung and McDonald’s.
“It should come as no surprise that brands have taken notice of this virtual influencer trend and want to make financial arrangements with (the representatives of) these virtual influencers,” the report observes.
Using these digital personas created using advanced real-time graphics offers several advantages, says Influencer Marketing Hub. They are more cost-effective than traditional celebrity endorsements, allowing brands to achieve significant marketing impact without the hefty price tag. Additionally, virtual influencers offer greater control over messaging and image, ensuring a consistent brand message. They can reach a wider audience than celebrities who are limited by their follower count, creating a unique way to form an emotional bond with target audiences, especially younger, tech-oriented demographics who are fascinated by the blend of technology and creativity. By curating influencer personalities for each target segment, brands can tailor their marketing efforts more precisely. Furthermore, virtual influencers provide integrated analytics, resulting in more accurate metrics and insights.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using virtual influencers. Businesses may have less control over virtual influencers than they initially think. Additionally, virtual influencers can be perceived as inauthentic or even creepy, which may alienate some audience segments. The lack of a human narrative can result in lowered engagement with the intended audience. Using virtual influencers offer high engagement for now because of the novelty, but it remains to be seen whether they will be a mainstay in the future.
Small But Mighty
Micro- and nano-influencers represent a powerful asset for brands looking to achieve meaningful and measurable impact. These influencers, with their highly engaged and loyal communities, offer substantial ROI, proving that bigger isn’t always necessarily better.
These micro-influencers consistently outperform their larger counterparts in terms of engagement. With engagement rates averaging 3.86%, micro-influencers far exceed the 1.21% engagement rate seen among mega-influencers who have more than one million followers.
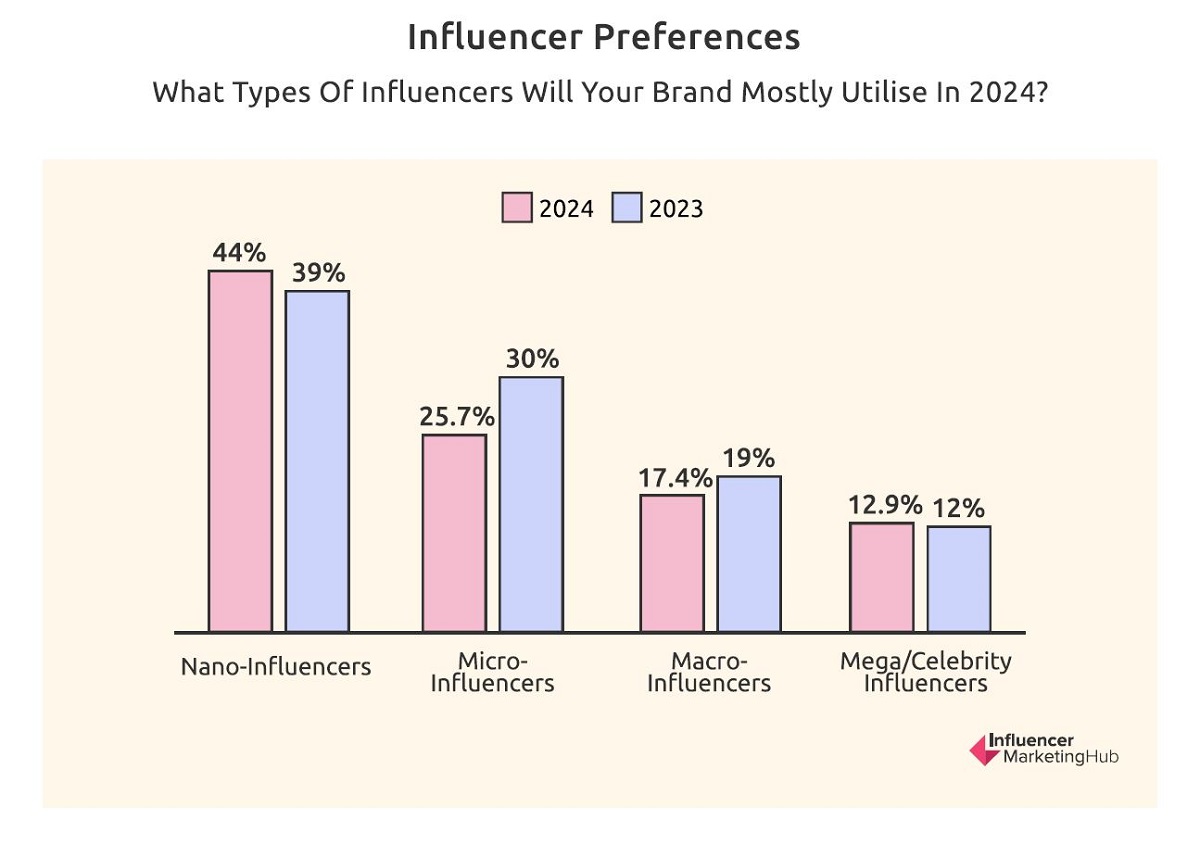
Influencer Marketing Hub found a strong preference for smaller influencers in its survey. Asked what size of influencer in terms of followers they were most likely to utilize, 44% of brands chose nano-influencers (1K-10K followers) as their most likely partners (up from 39%), followed by 25.7% opting for micro-influencers (10K-100K), down from 30%. In comparison only 17.4% of brands want to work with expensive macro-influencers (100K-1M), down from 19%, and only 12.9% are seeking partnerships with mega/celebrity influencers, up slightly from 12%.
But it’s not just about size — selecting the right social media platform also matters.
Instagram’s engagement rates range from 0.95% for accounts with more than 100K followers to 4.21% for accounts with fewer than 5K followers. In comparison, TikTok’s largest accounts with over 1M followers average 10.53% engagement, and small accounts with 1K-5K followers capture 15.04% engagement.
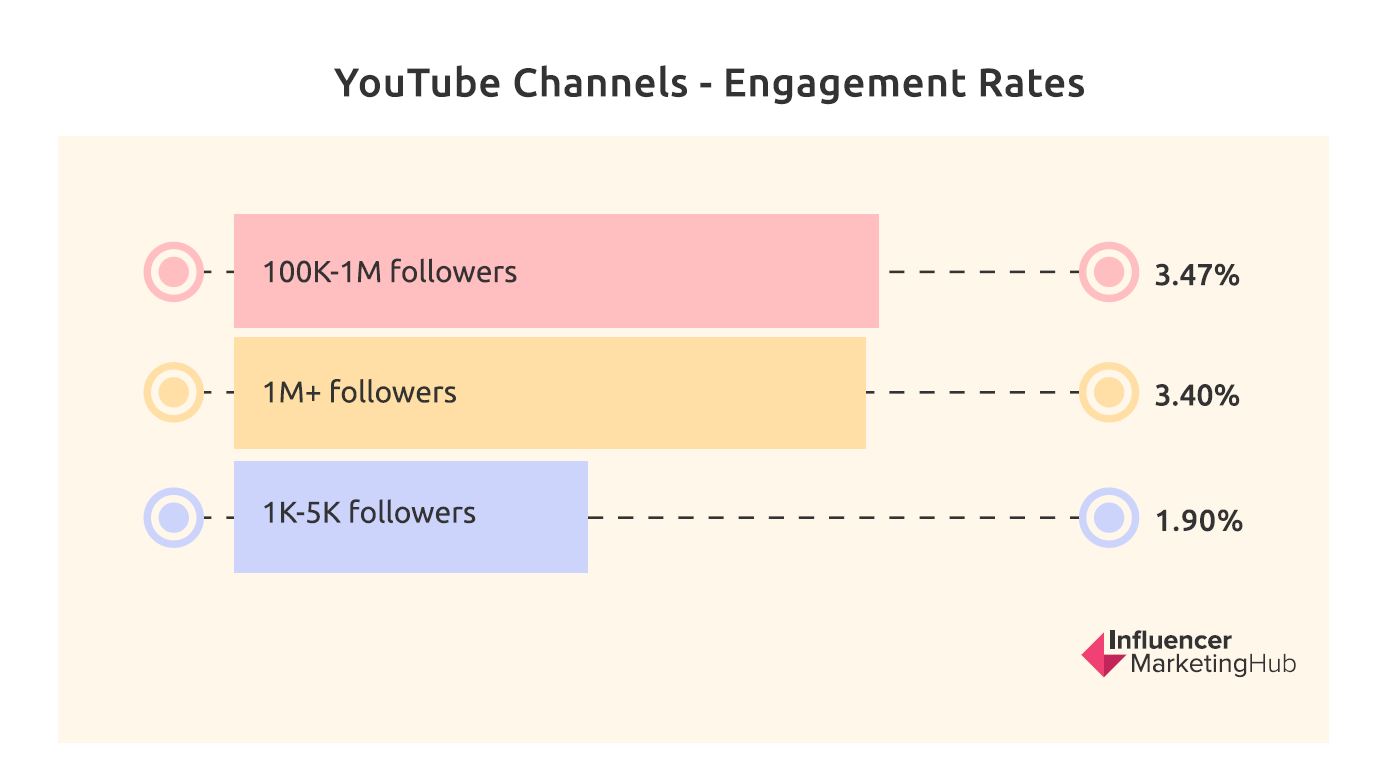
Conversely, larger YouTube channels have higher engagement rates than smaller channels. Technically, channels with 100K-1M followers have the highest engagement rate (3.47%), but huge YouTube influencers (1M+ followers) aren’t far behind (3.40%). Small YouTube channels with just 1K-5K followers, however, only manage an engagement of 1.90%.
Engagement is crucial to influencer marketing, but as the landscape becomes more crowded, the numbers are going down. Average engagement overall now stands at 2.05%, says Influencer Marketing Hub, down from 2.18% in 2021. However, it is close to 2019’s pre-COVID rate of 2.08%.
“We have seen a general reduction in engagement over the last few years, however, particularly for large accounts. Indeed, engagement for accounts with over a million followers (0.95%) is now less than half what it was in 2018 (1.97%).”
To maximize their marketing efforts, brands should adopt a strategic approach that includes investing in data-driven strategies and fostering authentic partnerships. By doing so, they can navigate the complexities of the influencer marketing ecosystem and achieve sustained success.
“The key to successful influencer marketing, is matching your brand with influencers whose fans are similar to your preferred customers and whose values match your own.”
READ MORE: The State of Influencer Marketing 2024: Benchmark Report (Influencer Marketing Hub)

Why subscribe to The Angle?
Exclusive Insights: Get editorial roundups of the cutting-edge content that matters most.
Behind-the-Scenes Access: Peek behind the curtain with in-depth Q&As featuring industry experts and thought leaders.
Unparalleled Access: NAB Amplify is your digital hub for technology, trends, and insights unavailable anywhere else.
Join a community of professionals who are as passionate about the future of film, television, and digital storytelling as you are. Subscribe to The Angle today!


