
READ MORE: The state of virtual production (Vū Technologies)
As virtual production bounces back from last year’s SAG-AFTRA strikes, adoption is skyrocketing. A new report from Vū Technologies, “The State of Virtual Production,” reveals how advancements in artificial intelligence and real-time graphics are shaping the future of the industry.
Rebounding and Innovating: Virtual Production’s New Era
The virtual production industry is undergoing a significant transformation in 2024, the report notes, rebounding robustly from the 2023 Hollywood labor strikes. The industry faced a dramatic 52% decline in production spending last year, but has since surged back with a remarkable 35% growth in the corporate and education sectors. Yet the outlook isn’t necessarily all roses — Vū finds there was also a 7% decrease in production spending in the entertainment sector over the same period last year.
Central to this resurgence are technological advancements in real-time computer graphics and AI-powered workflows. These innovations have reached a crucial inflection point, enabling creators to produce content with unprecedented speed and efficiency. Hybrid AI workflows in particular, Vū says, are making content creation up to 80% more efficient, revolutionizing the process for both seasoned artists and newcomers.
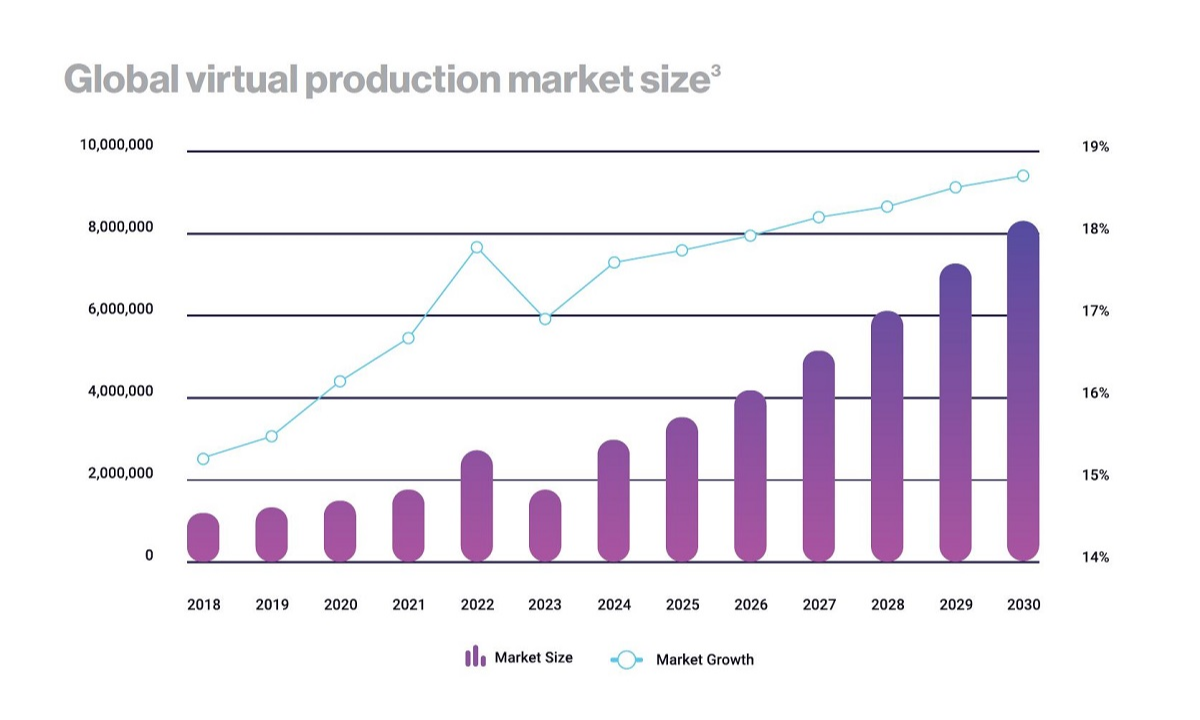
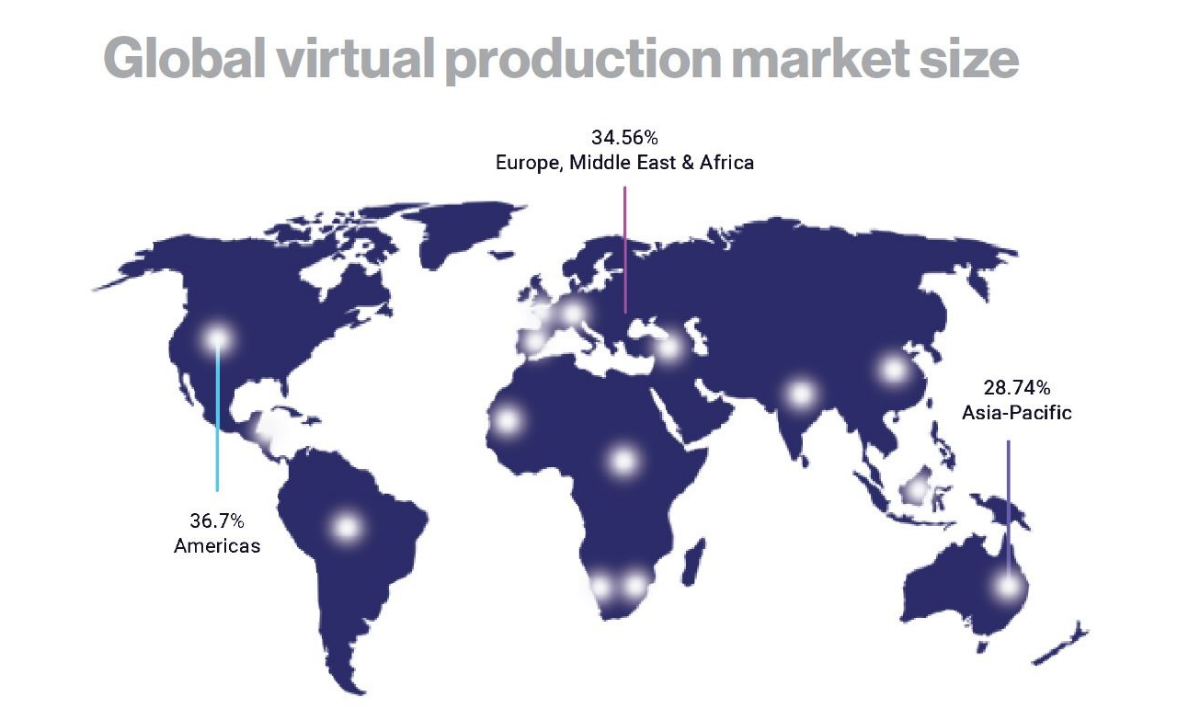
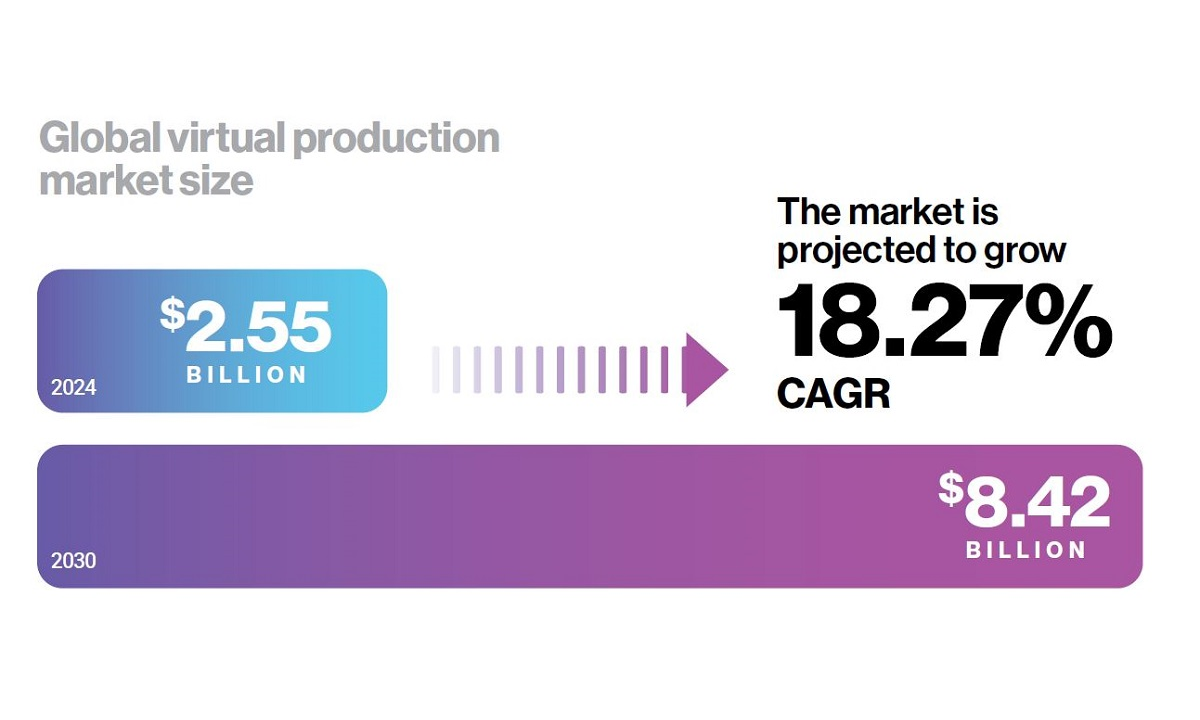
The market’s growth prospects are equally impressive. The global virtual production market is projected to expand to more than $8 billion by 2030, marking a 32% increase from initial 2020 projections. This surge, says Vū, is driven by the industry’s relentless innovation and its ability to integrate advanced technologies that democratize content creation, making sophisticated tools accessible to a broader range of creators.
From Experimentation to Standardization
Virtual production is evolving from experimental science to a more standardized and commercially viable industry, making the technology more accessible and practical for a wider range of users. According to the report, smaller, more versatile virtual production studios are becoming the norm, driven by constraints like ceiling height, available power, and system price.
By the end of 2022, there were an estimated 400 virtual studios worldwide. This number plateaued in 2023 due to the rapid market contraction following the strikes, but demand for smaller studios continues to grow in 2024, says Vū. These “micro-format” studios are expected to dominate the market, with thousands anticipated to launch by 2025.
The industry is crossing the “chasm” outlined by organizational theorist Geoffrey Moore, moving from early adopters to mainstream users who demand complete, convenient solutions. This shift is driven by the development of all-in-one virtual production systems that simplify the technology.
Rapid adoption of new tools and technologies, such as markerless tracking and 3D Gaussian Splatting, is allowing for quicker, more efficient creation of virtual environments. These advancements are paving the way for virtual production to become a mainstream method of content creation, “enabling artists to work faster and more creatively.”
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Path Ahead
While the virtual production industry is experiencing significant growth, it faces notable challenges. Initially, high costs and complexity were major barriers to adoption. Large investments in advanced LED systems and a steep learning curve deterred many potential users. Although costs have decreased, speed remains a critical challenge in fast-paced markets like advertising.
Another significant challenge is the ethical and regulatory landscape surrounding generative AI. Concerns about the use of copyrighted material and the potential for an AI “crash” are growing. Vū’s report highlights the possibility of a hype cycle crash, similar to previous technological booms and busts.
Despite these challenges, there are substantial opportunities on the horizon. Corporate studios that have adopted virtual production report significant increases in efficiency and output. Internal studios have seen a 56% increase in content output and a 72% reduction in production timelines. The elimination of travel and streamlined post-production processes are key factors contributing to these gains.
Furthermore, the concept of GenAI studios is emerging as a transformative opportunity. These studios integrate AI with virtual production, making the technology accessible even to those without technical expertise. By leveraging natural language processing and real-time visual communication, GenAI studios democratize content creation, allowing creators to bring their ideas to life quickly and efficiently.
Higher education is emerging as a significant growth sector for virtual production. Universities like the University of Florida are integrating advanced virtual production technologies into their campuses, using them for a variety of applications beyond education. These innovations provide new production efficiencies, enhance recruiting efforts, and break down barriers to access for fans and students alike.
“It’s always the people inside the industry that continue to reinvent it,” Vū Technologies founder Tim Moore says in a video presentation of the report. “Passion has a funny way of trumping logic. I’m betting on you guys to change the next couple of years in virtual production and take it to the moon.”

Why subscribe to The Angle?
Exclusive Insights: Get editorial roundups of the cutting-edge content that matters most.
Behind-the-Scenes Access: Peek behind the curtain with in-depth Q&As featuring industry experts and thought leaders.
Unparalleled Access: NAB Amplify is your digital hub for technology, trends, and insights unavailable anywhere else.
Join a community of professionals who are as passionate about the future of film, television, and digital storytelling as you are. Subscribe to The Angle today!


